
I noticed that some of the users are running Exchange Server 2007 Edge and public DNS Server on the same server.
Problem
There are some issues with services failing at start up if following is true:
- Exchange Server 2007, Exchange Server 2007 SP1, Exchange Server 2010 (Edge Role).
- Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2008 R2.
- DNS Server role is installed.
- Hotfix KB951746 is installed.
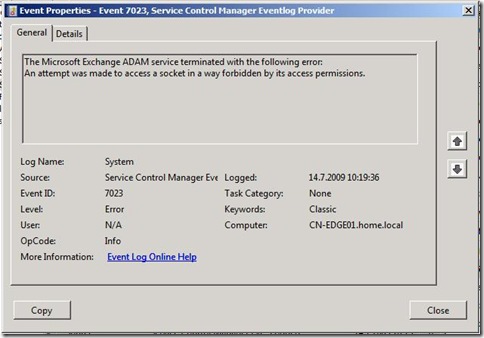
You receive following error and all Exchange services are stopped.
Log Name: System
Source: Service Control Manager
Date: 14.7.2009 10:19:36
Event ID: 7023
Task Category: None
Level: Error
Keywords: Classic
User: N/A
Computer: EDGE.exchange.pri
Description:
The Microsoft Exchange ADAM service terminated with the following error:
An attempt was made to access a socket in a way forbidden by its
access permissions.
So let’s start troubleshooting… ;-)
If we take a look with netstat we can see that DNS Service (dns.exe) is using 50636 port.

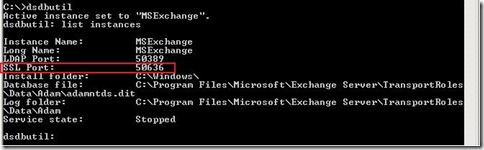
Exchange Server uses Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services (AD LDS), previous known as Active Directory Application Mode (ADAM), for storing Exchange (Organization)configuration. By default, the Edge Transport server uses the non-standard port 50636 for EdgeSync (Secure LDAP). We can check that with dsdbutil.
- Open cmd.exe, type dsdbutil and press Enter.
- Type list instances and press Enter.
Issue is with hotfix KB951746 (MS08-037: Description of the security update for DNS in Windows Server 2008, in Windows Server 2003, and in Windows 2000 Server (DNS server-side): July 8, 2008).
After security update KB951746 is installed on Windows Server 2008 (RTM/SP2), this issue occurs because the DNS server’s method of port allocation changes, and this change could prevent AD LDS from obtaining the port that it requires to function correctly.
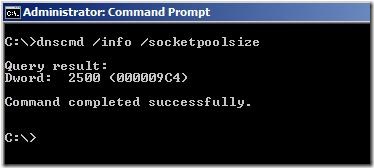
By default, after security update KB951746 is installed, the DNS server randomly allocates 2,500 UDP ports in the ephemeral port range. This is new behavior that is introduced by this update. A conflict may occur if one of these randomly allocated ports is a port that an AD LDS instance has to use.
We can check the size of socket pool with dnscmd:
Background information
To comply with Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) recommendations, Microsoft has increased the dynamic client port range for outgoing connections in Windows Vista and in Windows Server 2008. The new default start port is 49152, and the default end port is 65535.
We can check ephemeral port range in Windows Server 2008 witch netsh.
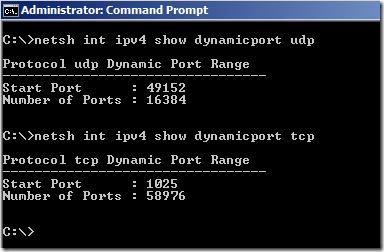
This is a change from the configuration of earlier versions of Microsoft Windows that used a default port range of 1025 through 5000.
In Windows Server 2003 or in Windows 2000 Server, the value of the MaxUserPort registry entry defines the ephemeral port range. The range is from 1024 to the value that is defined by the MaxUserPort registry entry.
After you install security update 953230 on Windows Server 2003 and down-level platforms, the following conditions are true:
- If the value of the MaxUserPort registry entry is set, the ports are allocated randomly from the [1024, MaxUserPort] range.
- If the value of the MaxUserPort registry entry is not set, the ports are allocated randomly from the [49152, 65535] range.
In Windows Server 2008:
- Ephemeral port allocation and the MaxUserPort registry entry:
In Windows Server 2008 or in Windows Vista, the value of the MaxUserPort registry entry signifies the number of ephemeral ports. The range is from the [start port, start range + MaxUserPort]. The default start port is port 49152.
- Effective ephemeral port range:
Ephemeral port allocation occurs in the [49152-65535] port range before you install security update 953230 on Windows Server 2008. This port allocation behavior does not change after you install security update 953230.
Solution for Windows Server 2003
We need to reserve Ephemeral port range for Exchange Server 2007 Edge AD LDS instance. We need to specify reserved ports in registry.
- Start regedit.exe
- Locate following registry key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Tcpip\Parameters
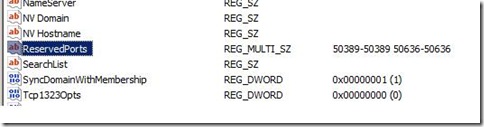
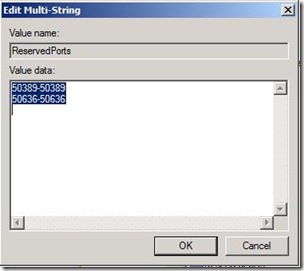
- Create New Multi-String Value with name ReservedPorts
- Enter following values for EDGE Ports that we want to exclude:
50389-50389
50636-50636
- Reboot server
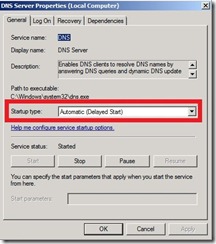
Solution for Windows Server 2008
Although we can change port range in Windows Server 2008 there is simple trick that does the job. We can change DNS Server service startup type to Automatic (Delayed Start).
Solution for Windows Server 2008 R2
Windows Server 2008 R2 DNS Server provides SocketPoolPortExclusionList that would allow us to exclude certain ports from DNS Server.
Dnscmd /Config /SocketPoolPortExclusionList
Exchange Server 2007 & Windows Server 2008 R2?
I was warned that mentioning Windows Server 2008 R2 in post of Exchange Server 2007 could be misleading (Thanks to Miha Pihler!). Some quick facts about Exchange Server 2007 and Windows Server 2008 R2:
- Exchange Server 2007 is NOT supported on Windows Server 2008 R2
- You need to deploy Update Rollup 9 for Exchange Server 2007 SP1 or SP2 for Exchange Server 2007 if you intend to run DC/GC servers on Windows Server 2008 R2
Links