 Did you try to backup Hyper-V Virtual Machines with Windows Server backup and received Event ID 521 error on Hyper-V host?
Did you try to backup Hyper-V Virtual Machines with Windows Server backup and received Event ID 521 error on Hyper-V host?
Backup started at '7.10.2008 23:21:14' failed as Volume Shadow copy operation failed for backup volumes with following error code '2155348129'. Please rerun backup once issue is resolved.

Event ID 12302 error on guest computer?
Volume Shadow Copy Service error: An internal inconsistency was detected in trying to contact shadow copy service writers. Please check to see that the Event Service and Volume Shadow Copy Service are operating properly.
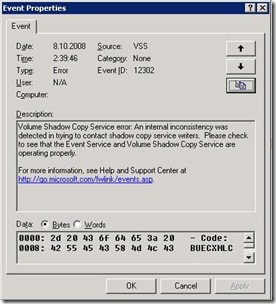
Result of running vssadmin list writers command is empty?

Event ID 10102 error appears in Microsoft-Windows-Hyper-V-VMMS/Admin Event Log?
Failed to create the backup of virtual machine 'GUEST01'. (Virtual machine ID 0FBA408B-B269-4169-9278-EC650FEEBB1B)

Solution resides in the registry ;).
Fix VSS Event ID 12302 on Hyper-v guests
In order to get rid off Event ID 12302 on Virtual Machines you need to follow the following procedure:
- Backup registry key:
HKLM\Software\Microsoft\EventSystem\{26c409cc-ae86-11d1-b616-00805fc79216}\Subscriptions
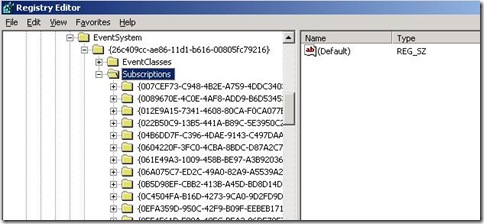
- Delete registry key Subscriptions.
- Restart Virtual Machine (key will be regenerated after restart).
- Verify that vssadmin list writers command returns valid list of writers.
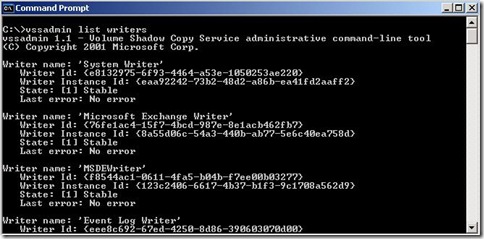
Enable Hyper-V VSS Writer with Windows Server Backup
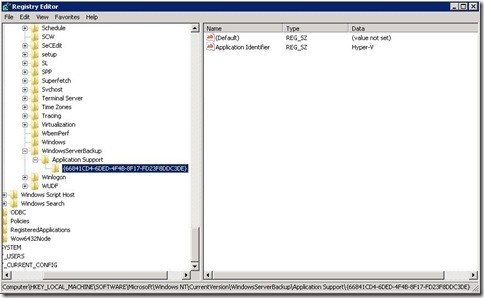
In order to enable VSS backups of Hyper-V Virtual Machines, you need to add the following registry keys and String Value to enable Hyper-V VSS Writer with Windows Server Backup on Hyper-V host.
Key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\
WindowsServerBackup\Application Support\{66841CD4-6DED-4F4B-8F17-FD23F8DDC3DE}
String Value:
Name: Application Identifier
Type: REG_SZ
Value: Hyper-V
Also check that Hotfix KB956697 (Windows Server 2008 Hyper-V VSS writer is not used during a backup job because of corrupted or invalid virtual machine configuration files.) is installed!
Microsoft Hyper-V Server 2008
I also have great news for all Hyper-V lovers. Microsoft released Microsoft Hyper-V Server 2008! The best thing about it is that it's FREE! Microsoft Hyper-V Server 2008 is a stripped version of Windows Server 2008 Core and contains only Windows Hypervisor, Windows Server driver model and virtualization components.
Microsoft® Hyper-V™ Server 2008 is a stand-alone product that provides a simplified, reliable, cost-effective and optimized virtualization solution enabling organizations to improve server utilization and reduce costs. It allows organizations to consolidate workloads onto a single physical server and is a good solution for organizations who want a basic and simplified virtualization solution for consolidating servers as well as for development and test environments. Low utilization infrastructure workloads, departmental applications and simple branch office workloads are also candidates to virtualize using Hyper-V Server 2008.
Links: